
Entry of a release factor into the A site terminates translation and the components dissociate.

As the mRNA moves relative to the ribosome, the polypeptide chain is formed. The large ribosomal subunit joins the small subunit, and a second tRNA is recruited. Translation begins when an initiator tRNA anticodon recognizes a codon on mRNA. coli translation apparatus takes only 0.05 seconds to add each amino acid, meaning that a 200-amino acid protein can be translated in just 10 seconds. As the ribosome steps across the mRNA, the former P-site tRNA enters the E site, detaches from the amino acid, and is expelled (Figure 2). The amino acid bound to the P-site tRNA is also linked to the growing polypeptide chain. The energy for each peptide bond formation is derived from GTP hydrolysis, which is catalyzed by a separate elongation factor.
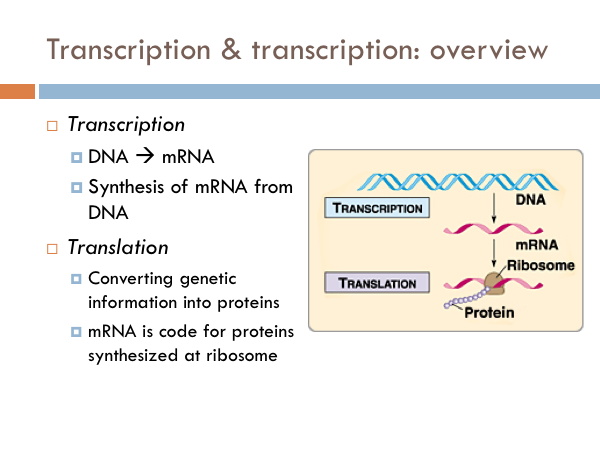
The formation of each peptide bond is catalyzed by peptidyl transferase, an RNA-based enzyme that is integrated into the 50S ribosomal subunit. Peptide bonds form between the amino group of the amino acid attached to the A-site tRNA and the carboxyl group of the amino acid attached to the P-site tRNA. The energy for each step of the ribosome is donated by an elongation factor that hydrolyzes GTP. Ribosomal steps are induced by conformational changes that advance the ribosome by three bases in the 3′ direction. In eukaryotes like you and me, the RNA is processed (and often has a few bits snipped out of it) to make the final product, called a messenger RNA or mRNA. If mRNA were not present in the elongation complex, the ribosome would bind tRNAs nonspecifically.Įlongation proceeds with charged tRNAs entering the A site and then shifting to the P site followed by the E site with each single-codon “step” of the ribosome. Basically, a gene is used to build a protein in a two-step process: Step 1: transcription Here, the DNA sequence of a gene is 'rewritten' in the form of RNA. As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, each mRNA codon comes into register, and specific binding with the corresponding charged tRNA anticodon is ensured.

Ribosome mRNA translationĭuring translation elongation, the mRNA template provides specificity.
#Dna transcription and translation steps free#
this creates an initiation complex with a free A site ready to accept the tRNA corresponding to the first codon after the AUG. The E (exit) site releases dissociated tRNAs so that they can be recharged with free amino acids. The P (peptidyl) site binds charged tRNAs carrying amino acids that have formed peptide bonds with the growing polypeptide chain but have not yet dissociated from their corresponding tRNA. coli consists of three compartments: the A (aminoacyl) site binds incoming charged aminoacyl tRNAs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
